Introduction
The Custom Views enables you to define, save, and execute advanced queries over trace data using a SQL-like syntax. With Custom Views, you can explore trace data in a way that fits the needs by selecting specific fields, applying aggregations, defining aliases, and grouping results.
To view the details:
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Traces.
- Click the menu in the left right corner.
- In My Traces Views, select Custom Views.

The following are the key functionalities.
Field Selection
Allows you to choose the fields such as app, service, operation, or tags like url.path, infra.group, and so on.
Example:
- Pattern-Based Filtering and Grouping
select service
where app =~ 'defau' AND infra.group =~ 'NO_GR'
groupBy (service)
Returns services where the app name contains “defau” and infra.group matches “NO_GR”.
Results are grouped by service.
- Multi-Field Selection and Grouping
select service, operation, url.path
where app IN ('default')
groupBy (service, operation, url.path)
Retrieves unique combinations of service, operation, and url.path for the “default” app.
Useful for breaking down traffic by endpoint.
Aggregation
Allows you to summarize your data by applying the functions to selected fields.
Note
Only the aggregation functionscount, sum, avg, min, and max are supported.Example:
SELECT service, operation,count(*) as spanCount where app = 'default' AND (service = 'frontend' OR service = "frontend-proxy") groupBy(service,operation)
Returns span count against each combination of service and operation that contain the app “default” and service is either frontend or frontend-proxy.
Derived Fields
You can calculate aggregates using arithmetic, such as: error rates and throughput.
Example:
select app,
service AS svc,
operation AS op,
count(*) AS spanCount,
avg(durationUs) AS avgLatency,
(sum(error) / count(*)) * 100 AS errorRate
groupBy (app, service, operation)
Shows total spans, average latency, and error rate by app, service, and operation.
Fields are aliased for clarity.
Grouping
Allows you to group results by one or more fields.
Example:
- Pattern-Based Filtering and Grouping
select service
where app =~ 'defau' AND infra.group =~ 'NO_GR'
groupBy (service)
Returns services where the app name contains “defau” and infra.group matches “NO_GR”.
Results are grouped by service.
- Multi-Field Selection and Grouping
select count(service)
where app IN ('default')
Returns the total number of spans that contain a service value for the app default.
Filtering
SELECT
operation,
avg(durationUs) AS averageLatency
where app IN ('uat') AND service STARTSWITH 'dash-streaming'
groupBy (operation)
Returns operations, averageLatency from services whose name starts with dash-streaming.
Supported Operators in Where clause:
Equals (=)
Example: app = “default”
Matches trace data where the app is exactly “default”.
Not Equals (!=)
Example: app != “default”
Matches trace data where the app is not “default”.
Regex Match (=~)
Example: app =~ “default”
Matches trace data where the app matches the regex pattern “default”.
Not Regex Match (!~)
Example: app !~ “default”
Matches trace data where the app does not match the regex pattern “default”.
Combining Multiple Filters
Logical operators allow users to create more refined queries:
AND (AND)
Example:
app = “default” AND service = “frontend” Returns trace data where the app is “default” and service is “frontend”.
OR (OR)
Example: app = “default” OR app = “uat”
Returns trace data where the app is either “default” or “uat”.
**Grouping with Parentheses
Example: app = “default” AND (service = “frontend” OR service = “frontend-proxy”)
Returns trace data where the source is “agent” and the service is either “frontend” or “frontend-proxy”.
Using the IN and NOT IN Operators
These operators allow checking against multiple values, supporting both plain strings and regex patterns:
Match Exact Values
Example: app IN (“default”, “uat”)
Matches trace data where the app is “default, “uat”
Exclude Specific Values
Example: source NOT IN (“default”, “uat”)
Excludes trace data where the app is “default, “uat”
Note
Values in IN/NOT IN can be only strings.Data Greater Than (>) and Less Than (<)
Example: durationUs > 500000000 and durationUs < 500000000
Matches trace data where the latency (durationUs) is greater than 5 and less than 60 milliseconds.
Aliases
Use AS to rename output fields for readability. Aliases are recommended for clarity.
Note
For any function, query result size is limited (default: 100 rows). If the result exceeds the limit, the system displays an error to refining your query.The Custom Views enables you to save the view and reuse it.
To save the view, click SAVE VIEW.

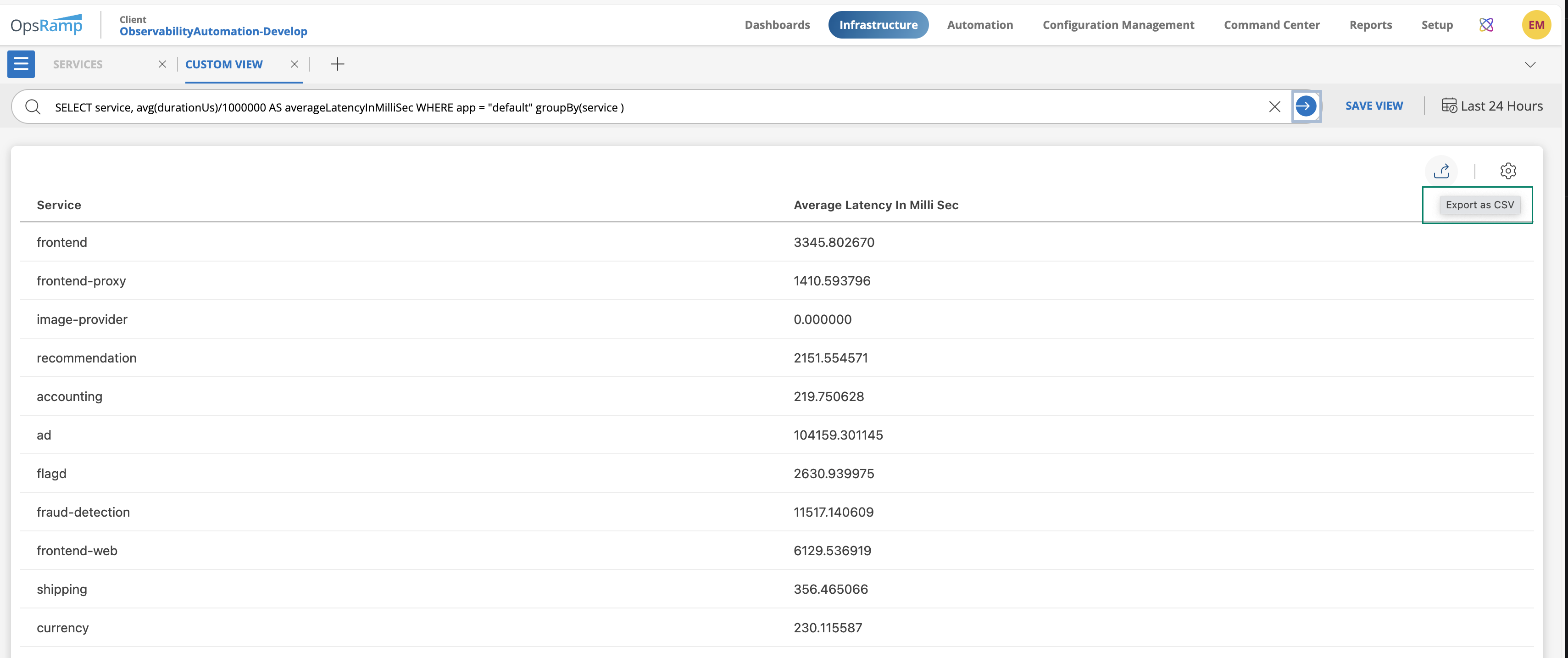
The Custom Views now allows users to easily copy data and export selected datasets. When you hover over a value, a copy option appears, enabling you to copy the data. To export specific datasets, click Export as CSV.